Abstract
Background:
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is the most common genetic disorder in the United States, seen in 100,000 Americans. SCD complications include pain episodes, chronic anemia and long-term end organ damage, leading to significant impairment in health-related quality of life (HRQOL) across the lifespan. Hydroxyurea (HU) reduces morbidity and mortality, improves HRQOL and lowers healthcare utilization, yet adherence remains suboptimal. Limited evidence from cross-sectional studies demonstrates an association between lower HU adherence and worse HRQOL scores.
Objective:
To assess the longitudinal relationship of HU adherence to HRQOL domains, including fatigue and depression. We hypothesized that higher HU adherence over time would be associated with improvement in HRQOL domain scores, especially depression and fatigue.
Methods:
In this longitudinal cohort study (NCT04675645), patients were enrolled from the comprehensive sickle cell clinic at Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago. Patients were eligible if they were ³8 years old, had SCD (any genotype), and on HU with a stable dose for ³2 months. Study assessments included PROMIS ® measures for depression and fatigue, self-report of adherence using visual analogue scale (VAS), and patient demographics. Assessments were completed at baseline and every 3 months with a total of 5 visits (0, 3, 6, 9 and 12 months). Laboratory markers of adherence collected from chart review, including fetal hemoglobin (HbF%) and mean corpuscular volume (MCV). We conducted bivariate correlations among demographic variables, adherence markers and HRQOL scores as well as among adherence variables (VAS, HbF, MCV) at each visit. We conducted different multilevel models (MLMs), fixed and random effects, to understand the extent to which between- and within-person variation in adherence was associated with HRQOL scores over the 12-month period. We report unstandardized betas (B) and 95% Confidence Intervals (CI) from the MLMs.
Results:
Twenty-three patients have been enrolled (96% HbSS, 65% females, 100% Black, median age 15 [range 9-22] years old). At baseline, participants had a median Hb level of 9.5 (IQR 8.3-10.3 g/dl) with a HbF of 16.4% (IQR 13.1-28.7%) and MCV of 106.5 fl (IQR 91.6-113.9 fl). Participants' MCV levels significantly correlated with HbF% and VAS at visit 1 (r=0.58, P <0.01; r=0.6, P <0.01), visit 2 (r=0.66, P <0.01; r=0.63, P <0.01), visit 4 (r=0.76, P <0.01; r=0.72, P <0.01) and visit 5 (r=0.71, P <0.01; r=0.59, P <0.05), respectively. Participants' VAS adherence levels significantly increased from visit 1 to visit 5 (median 72 [IQR 60-92] vs. 88 [IQR 75-95], P=0.04, respectively) along with significant improvement in their fatigue scores (median 52.8 [IQR 35.1-70.5] vs. 30.8 [IQR 13.2-48.4], P=0.001, respectively).
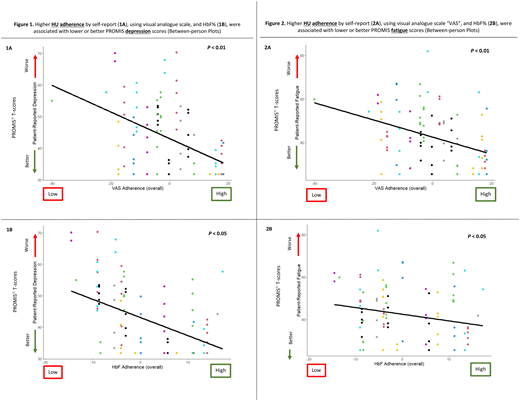
Variation in fatigue and depression scores across the study period was due to between-person differences (38% and 71%, respectively) or within-person fluctuations (62% and 29%, respectively). Using fixed and random effect MLMs, between-person differences in HU adherence over 12 months using VAS and HbF% were significantly related to participants' reported depression (B -0.43, 95% CI -0.69 to -0.17, P <0.01; B -0.58, 95% CI -1 to -0.15, P <0.05, respectively) (Figure 1) and fatigue scores (B -0.42, 95% CI -0.68 to -0.16, P <0.01; B -0.43, 95% CI -0.78. to -0.06, P <0.05, respectively) (Figure 2). In contrast, we found no statistically significant effects of within-person variation in adherence, using VAS and HbF, on participants' reported fatigue and depression scores over 12 months, which could be due our small sample size.
Conclusions:
Children and adolescents who were more adherent to HU across the entire study period were less likely to experience fatigue and depression, compared to those who were less adherent. Participants' self-report and laboratory markers of adherence were significantly correlated across study visits. Within-person fluctuations in adherence were not associated with changes in fatigue and depression scores across the study period. Future multi-institutional studies with a larger sample size are needed to better understand the within-person effects of variation in HU adherence on HRQOL scores over time. Behavioral interventions, such as mHealth apps, that are focused on improving HU adherence among children and adolescents with SCD has the potential to improve HRQOL and other important health outcomes.
Badawy: Bluebird Bio Inc: Consultancy; Vertex Pharmaceuticals Inc: Consultancy; Sanofi Genzyme: Consultancy. Thompson: Biomarin: Research Funding; Baxalta: Research Funding; bluebird bio, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene/BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; CRISPR Therapeutics: Research Funding; Vertex: Research Funding; Editas: Research Funding; Graphite Bio: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Agios: Consultancy; Beam: Consultancy; Global Blood Therapeutics: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Cella: FACIT: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal